Leverage the power of aged and expired domains for your SEO.
We have curated a huge inventory of pre-qualified, ready-to-transfer domains with strong link profiles for almost any niche and language imaginable.
All domains are ready for transfer and perfect for money sites, PBNs, 301s or AI sites.
- 6000+ top TLD domains (com/net/org)
- 3000+ ccTLD domains (uk/de/nl/at/fr and many more)
- Filterable by DA, DR, Price, TLD, Niche and Language
- Link data insights for each domains
How it works
#1 Check out our domain list
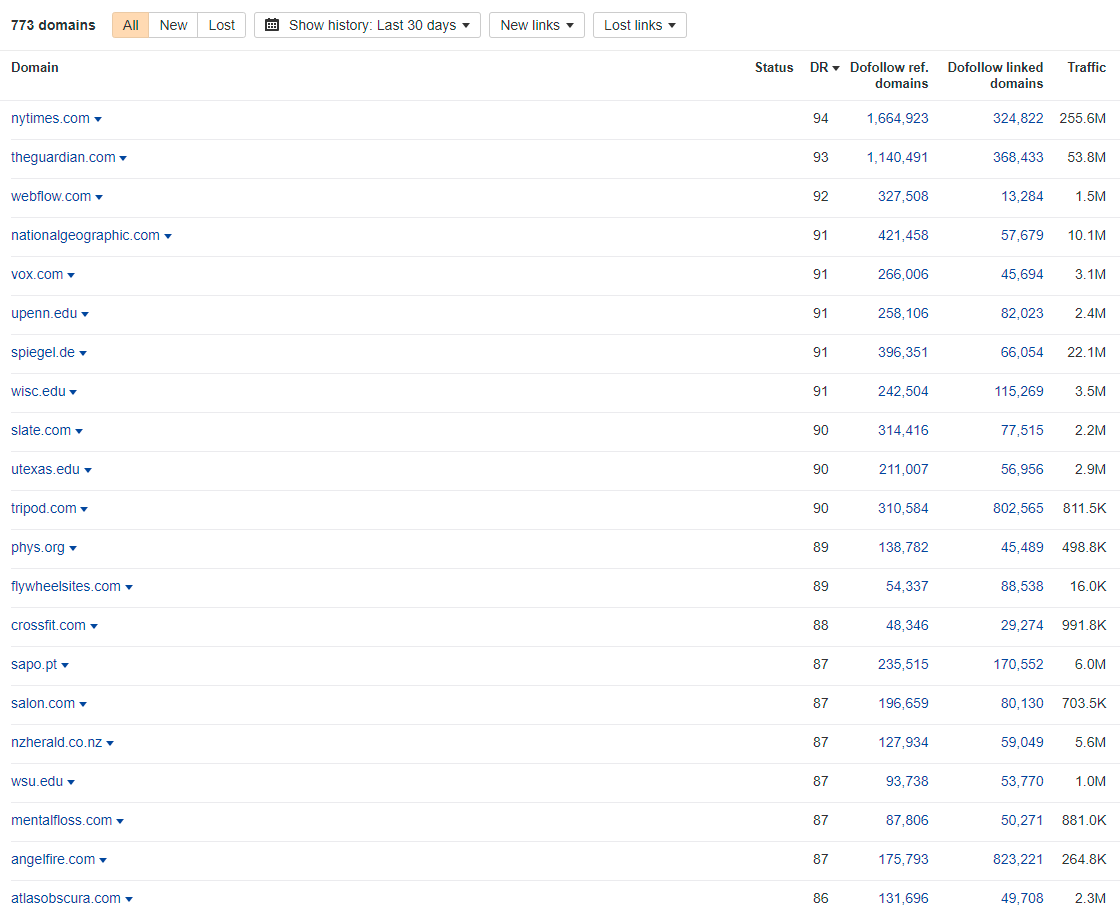
- Start by exploring our extensive domain list. This list features a wide variety of aged domains, including top TLDs and ccTLDs.
- Each domain comes with detailed metrics such as DA, DR, and its backlink profile, allowing you to assess its potential impact on your SEO goals.
- Focus on finding a domain that aligns well with your specific goals, whether it’s for branding link building, 301s, money sites etc.
#2 Get in touch with us
- Once you’ve identified a domain that fits your needs, the next step is to get in touch with us. You can do this easily via email or through our Discord channel.
- We’ll provide you with all the necessary details about the domain and the purchase process.
- After finalizing your choice, proceed with the payment for the domain. We offer various payment methods for your convenience and ensure a secure transaction process, including Paypal, Stripe and Wise + SEPA (for EU only). Invoices are supplied, of course.
#3 Domain Transfer
- After the payment is confirmed, we’ll initiate the final transfer of the domain to you.
- We will provide you with an authorization code (auth code) which you can use to transfer the domain to your preferred registrar.
- In some cases, if it’s more convenient and feasible, we can directly push the domain to your registrar account.
- We ensure that this process is smooth and hassle-free, providing assistance throughout to make sure the transfer is successful.
Why are aged domains so powerful?
-
Age: The age of a domain is a crucial factor. Search engines, especially Google, tend to trust older domains more than new ones. This trust factor can lead to quicker indexing and a perception of authority.
-
Authority (DA/DR): Aged domains often come with established Domain Authority (DA) and Domain Rating (DR). High DA/DR indicates that a domain is likely to rank well in search engine results, making these domains valuable for SEO.
-
Link Profiles (Referring Domains – RD): One of the most significant advantages of aged domains is their established link profiles. These domains usually have links from other reputable sites, enhancing their SEO value significantly.
-
Relevance: Aged domains can offer high relevance, especially if they have been associated with a particular industry or niche. This relevance can be leveraged for SEO and marketing purposes.
-
Branding Possibilities: Many aged domains have unique names that can be excellent for branding. A memorable domain name can be a valuable asset for any business.
-
No “Google Sandbox”: New domains often go through a period where they don’t rank well in Google, known as the “Google Sandbox.” Aged domains typically bypass this phase, allowing for quicker SEO results.
| SEO Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| High Metrics (DA/DR) | Aged domains often have established DA/DR, indicating potential for strong search engine performance. |
| Link Equity | The existing backlinks of aged domains can pass significant link equity to associated sites. Where else could you get links from NY Times, Guardian, BBC, VOX or Nationalgeopgraphic? Right, nowhere. |
| Age | Older domains are often viewed more favorably by search engines, leading to quicker indexing and ranking. |
| Authority | Established authority makes aged domains more credible and trustworthy in the eyes of search engines. |
| Relevance | Relevant aged domains can drastically improve rankings in specific niches or industries. |
Why you should buy aged domains from us.
-
Pre-screened Domains: Every domain in our inventory has been thoroughly pre-screened for quality, ensuring they meet high standards of DA/DR, clean link profiles, and more.
-
Extensive Selection: Choose from over 10,000 aged domains, offering a wide range of options to find the perfect fit for your needs. Top TLDs and ccTLDs.
-
Incredible Link Profiles: Our domains include links from prestigious sites like NYtimes, Guardian, BBC, Vogue, etc., offering unparalleled SEO value.
-
Affordable: We offer competitive pricing, making high-quality aged domains accessible without breaking the bank.
-
No Haggling at Domain Auctions: Avoid the hassle and uncertainty of domain auctions with our straightforward, transparent pricing.
How to use aged domains for SEO.
Money Sites
- Avoid the “sandbox”: When launching a new website, starting with an aged domain can give you a significant advantage in SEO. Unlike new domains, aged domains are often already recognized and trusted by search engines, which can lead to faster indexing and better initial rankings.
- Established Authority: Aged domains typically come with a history and established authority, which can be advantageous if the domain has maintained a positive reputation. This pre-existing authority can lend credibility to your new site, which is crucial in today’s competitive digital landscape.
- Brand Recognition: Sometimes, aged domains have brandable and memorable names, which can be a boon for marketing and building a brand identity. A well-chosen domain name can make your website more memorable to users and may enhance marketing efforts
Private Blog Networks (PBNs)
- Building Authoritative Backlinks: Aged domains can be used to create a network of authoritative sites (PBNs) that link back to your main website. Since these domains come with strong backlink profiles, they can pass significant link equity to your site.
- Control Over Content: With PBNs, you have complete control over the content and backlinks. This allows for the creation of highly relevant and niche-specific content that can link back to your main site, enhancing its relevance and authority in your industry.
- Strategic SEO Asset: Properly managed and setup PBNs can be a powerful strategic asset in your SEO toolkit. They offer a way to consistently build high-quality backlinks that no one else can get.
301 Redirections
- Transferring Link Equity: One of the most common uses of aged domains is to implement 301 redirects, which effectively transfer the link equity from the aged domain to your existing website. This can result in an immediate boost in your site’s authority and rankings. For more information on how to use 301s correctly read this guide.
- Merging Niche Relevance: If the aged domain is relevant to your website’s niche, redirecting it can enhance your site’s relevance in that niche. This can be particularly effective if the aged domain has a strong backlink profile from authoritative sites in your industry.
FAQ
For successfully transferred domains, we don’t offer any refunds. All sales are final.
The domain list is updated at least once every two weeks. So you should check back frequently to see any new domains.
After you’ve paid for the domain of your choice, we will start the domain transfer.The domain(s) will be pushed to your accounts at the registrar that fits best. We’ll provide guidance during these steps to make sure everything goes smoothly and without hiccups.Once you have the authorization code, the transfer should only take a few hours to max. 2 days.
While all domains go through a thorough vetting process, we still recommend that you check and analyze the domain yourself, before buying.In our PBN guide we show you exactly how to do that – click here for Domain Analysis
For top TLDs like .com, .net, .org you can use one of the reputable registrars like Namecheap, Dynadot, Name.com, Namesilo, InternetBS etc. – we don’t generally recommend GoDaddy.For ccTLDs there are usually preferred registrars that you should use. InternetBS is usually a good choice here, too.
That’s a good question. And we have just the right answer for it: Read our PBN guide. No, seriously. We dedicated a huge section in our PBN guide to just hosting. We guide you through the whole process on how to host your new expired domain without any virtual footprints.Trust us, it’s worth reading.
Sure, no problem. Just fill out the form and we’ll send you a curated list of available domains in your niche that you can then manually check yourself.
Yes, all of the domains are already registered. This guarantees that we can transfer the domain to you in a jiffy and without compromises.
We can accept Paypal, Stripe or SEPA (Bank Transfers). For domains >2500 USD we use Escrow (if needed).